
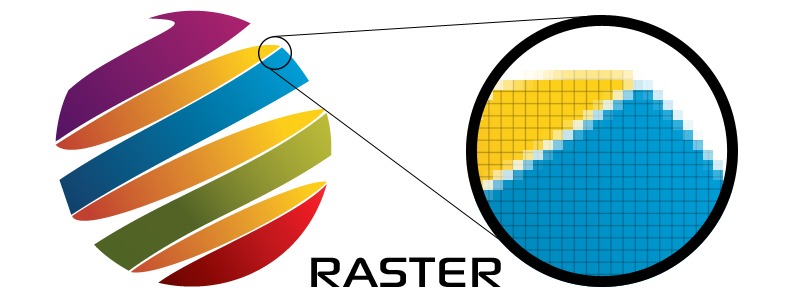
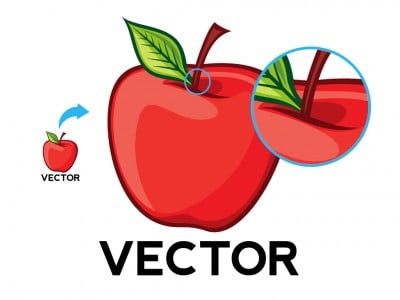
BMP, TIFF, GIF and JPEG are some of the raster image file formats available. Fortunately, there are already image compression techniques and algorithms that have been made to address that problem. Discuss web design long enough and the words raster and vector are bound to come up. Together, they’re worth a thousand words. Individually, these pixels are worthless. Each square, or pixel, is coded in a specific hue or shade. Since raster graphics store much information, they require large file sizes and they can be a bit of a hassle to work with. Raster graphics render images as a collection of countless tiny squares. Vector graphics are better suited for typesetting and graphic design. Vector graphics, on the other hand, is able to scale up to any resolution because of it uses geometry and mathematical equations to define images rather than directly mapping pixels in a grid. The image will look blocky and pixelated. It can be scaled down with no changes in quality, but when the resolution is scaled up, quality loss is unavoidable. The main disadvantage of raster graphics is that it is dependent on resolution. The word raster was borrowed from the term ‘raster scan,’ which was how old CRT monitors displayed images, by magnetically steering a concentrated electron beam line by line to form an image.
#Raster graphics definition full#
This means that an image with a 1280×720 resolution will contain 921,600 pixels while a full HD 1920×1080 image will have 2,073,600 pixels, which will obviously give it a bigger file size when compared to the former.

#Raster graphics definition software#
Learn more about Kornit’s RIP software solutions, and discover unparalleled printing quality, speed and performance.The file size of a raster image depends also on the size of the image, which is determined by the number of pixels being used in the image. RIP ensures reliable color reproduction, saves time in the long run and reduces waste due to multiple reprints. This image illustrates the difference between bitmap and vector images. Raster graphics render images as a collection of. In computer graphics, image tracing, raster-to-vector conversion or raster vectorization is the conversion of raster graphics into vector graphics. The quality of the RIP software directly determines the quality of the output. A bitmap is a grid of individual pixels that collectively compose an image.

Bitmap-based images are comprised of pixels in a grid. The RIP is an important component in the printing process as it determines the color, screen pattern and resolution of the printed product. Bitmaps and raster images are the same thingbut different from vectors.
The RIP can also be used to enlarge images for printing without loss of detail since it increases the file resolution. A powerful ICC color profile management maximizes the color gamut of the inks. In addition, most RIP software come with ICC (International Color Consortium) color profilers and allow color management. RIP software enables handling many file types and file sizes. The RIP software processes multiple content types for a specific print environment and communicates that processed data to the printer for final output. Animated GIF and MPEG2 payloads are considerably larger, but their formats have the advantage of streaming playback. However, the APNG payload is still about 10 times bigger than Lottie. The raster image is similar to the pixels on the computer screen. Its output outperforms that of our hypothetical raster animation encoder by a margin of about 20 due to the APNG’s compression algorithm. A raster image processor (RIP) is a software that translates (rasterizes) computer vector files (InDesign, Illustrator, Photoshop, PDF, JPG, etc.) to a raster image also known as bitmap that is composed out of a matrix of dots that the printer can understand and print.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
